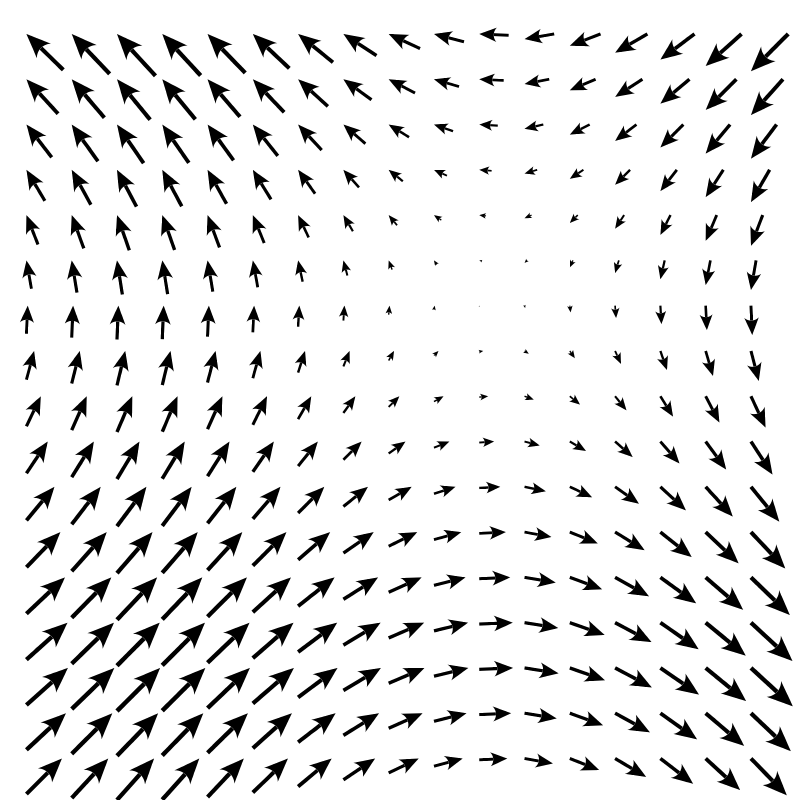
Arrows of a vector field.
> import Diagrams.Backend.SVG.CmdLine> {-# LANGUAGE NoMonomorphismRestriction #-}
> {-# LANGUAGE FlexibleContexts #-}
> import Diagrams.Prelude> locs = [(x, y) | x <- [0.1, 0.3 .. 3.25], y <- [0.1, 0.3 .. 3.25]]Create a list of points where the vectors will be placed.
> points = map p2 locsThe function to use to create the vector field.
> vectorField (x, y) = r2 (sin (y + 1), sin (x + 1))
>
> arrows = map arrowAtPoint locs
>
> arrowAtPoint (x, y) = arrowAt' opts (p2 (x, y)) (sL *^ vf) # alignTL
> where
> vf = vectorField (x, y)
> m = norm $ vectorField (x, y)
>
> -- Head size is a function of the length of the vector
> -- as are tail size and shaft length.
>
> hs = 0.02 * m
> sW = 0.004 * m
> sL = 0.05 + 0.1 * m
> opts = (with & arrowHead .~ spike
> & headLength .~ normalized hs
> & shaftStyle %~ lwN sW)
>
> field = position $ zip points arrows
>
> example = ( field # translateY 0.05
> <> ( square 3.5 # lw none # alignBL))> main = mainWith (example :: Diagram B)