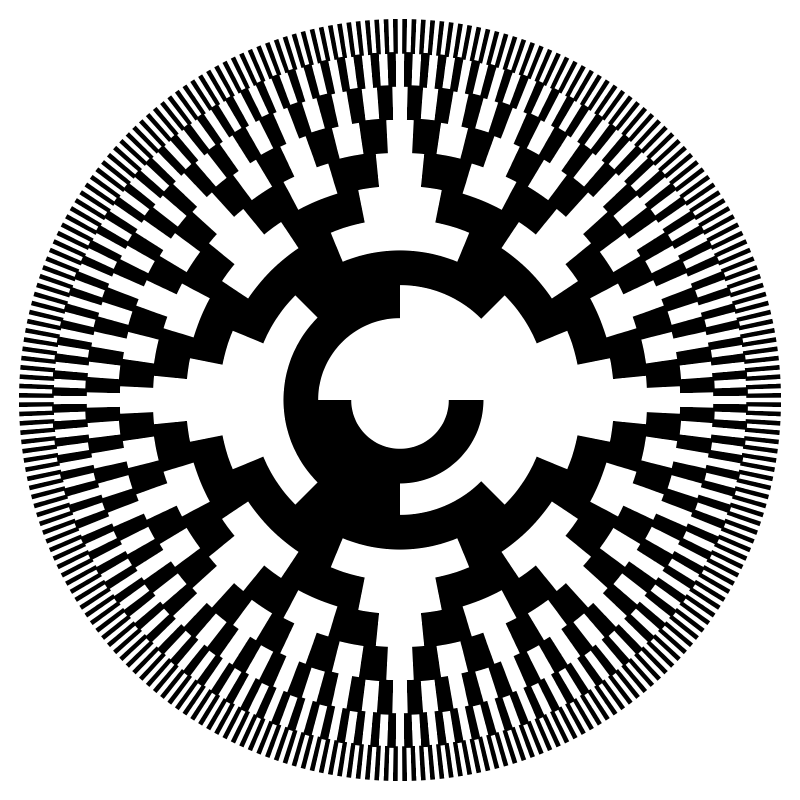
Circular gray code, like that used on some rotational sensors.
> import Diagrams.Backend.SVG.CmdLine> {-# LANGUAGE NoMonomorphismRestriction #-}
> import Diagrams.Prelude hiding (gray)
> import Data.List.Split (chunksOf)
> import Data.Maybe (catMaybes)
> import Control.Applicative
> import Data.Monoid (mconcat)
> import Data.List (transpose)gray n recursively generates an n-bit Gray code, where each n-bit binary number differs from the next in exactly one position.
> gray 0 = [[]]
> gray n = map (False:) g ++ map (True:) (reverse g)
> where g = gray (n-1)Construct a circular diagram from the n-bit gray code: each bit position corresponds to a concentric ring, with black/white indicating 0/1. ringOffsets converts a list of booleans into a list of angular segments corresponding to consecutive runs of True.
> rings n = mkRingsDia . map ringOffsets . transpose . gray $ n
> where ringOffsets :: [Bool] -> [(Direction V2 Double, Angle Double)]
> ringOffsets = map l2t . chunksOf 2 . findEdges . zip [rotate α xDir | α <- [0 @@ turn, 1/(2^n) @@ turn .. fullTurn]]
> l2t [x,y] = (x, angleBetweenDirs x y)
> l2t [x] = (x, angleBetweenDirs x xDir) -- arc angle will never be > fullturn ^/ 2
>
> findEdges :: Eq a => [(Direction V2 Double, a)] -> [Direction V2 Double]
> findEdges = catMaybes . (zipWith edge <*> tail)
> where edge (_,c1) (a,c2) | c1 /= c2 = Just a
> | otherwise = NothingGenerate concentric circular arcs from lists of angular segments.
> mkRingsDia = mconcat . zipWith mkRingDia [2,3..]
> where mkRingDia r = lwL 1.05 . mconcat . map (strokeP . scale r . uncurry arc)
>
> example = pad 1.1 (rings 10)> main = mainWith (example :: Diagram B)