Until now packing of widgets has been done either through
sequencing in horizontal or vertical boxes, or in a table. You
can, however, also place widgets in any position you like,
using a
Fixed or a
Layout widget. Use of the
Fixed container is not recommended, because it does
not resize well.
The Layout container is similar to the Fixed container
except that it implements an infinite (where infinity is less
than 2^32) scrolling area. The X window system has a limitation
where windows can be at most 32767 pixels wide or tall. The
Layout container gets around this by doing some
exotic stuff using window and bit gravities, so that you can
have smooth scrolling even when you have many child widgets in
your scrolling area. Since it is used in a scrolled window, the
disadvantages of the
Fixed widget do not apply.
A Layout container is created using:
layoutNew :: Maybe Adjustment -> Maybe Adjustment -> IO Layout
As you can see, you can optionally specify the Adjustment objects that the Layout widget will use for its scrolling.
You can add and move widgets in the Layout container using the following two functions:
layoutPut :: (LayoutClass self, WidgetClass childWidget) => self -> childWidget -> Int -> Int -> IO () layoutMove :: (LayoutClass self, WidgetClass childWidget) => self -> childWidget -> Int -> Int -> IO ()
The first argument is the x position, the second the y position. The top left is (0,0), x grows from left to right, and y from top to bottom.
The size of the
Layout container can be set using the next
function:
layoutSetSize :: LayoutClass self => self -> Int -> Int -> IO ()
The first argument is the width of the entire scrollable area, the second the height.
In the example we place a list of labels, each with an upper case letter of the alphabet, in a circle around a chosen centre. The labels are positioned perpendicular to the radius using the Gtk2Hs function:
labelSetAngle :: labelClass self => self -> Double -> IO ()
The angle is in degrees, measured counterclockwise.
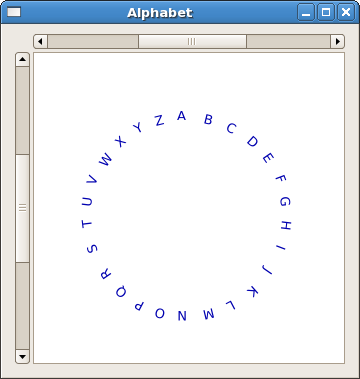
The layout widget is placed into a scrolled window with
containerAdd because it is scrollable, and so does
not need a view port, as in Chapter 6.1. The labels are
positioned using angular coordinates, which are then
transformed into Cartesian coordinates with the Prelude
sin and
cos functions. These take radians as their
arguments (between 0 and (2 * pi)). Width and Height in the
example are parametrized, as is the list to be displayed.
Furthermore, in
main the corners of the
Layout are marked, so you can easily experiment with its
size, if you want. Note that the actual marker has been replaced with '+' here, because
the validator complained.
import Graphics.UI.Gtk
main :: IO ()
main = do
initGUI
window <- windowNew
set window [windowTitle := "Alphabet" , windowDefaultWidth := 350,
windowDefaultHeight := 350 , containerBorderWidth := 10]
sw <- scrolledWindowNew Nothing Nothing
set sw [scrolledWindowPlacement := CornerBottomRight,
scrolledWindowShadowType := ShadowEtchedIn,
scrolledWindowHscrollbarPolicy := PolicyAutomatic,
scrolledWindowVscrollbarPolicy := PolicyAutomatic ]
containerAdd window sw
layt <- layoutNew Nothing Nothing
layoutSetSize layt myLayoutWidth myLayoutHeight
widgetModifyBg layt StateNormal (Color 65535 65535 65535)
containerAdd sw layt
upleft <- labelNew (Just "+(0,0)")
layoutPut layt upleft 0 0
upright <- labelNew (Just ("+(" ++ (show (myLayoutWidth - 50)) ++",0)"))
layoutPut layt upright (myLayoutWidth -50) 0
dwnright <- labelNew (Just ("+(0," ++ (show (myLayoutHeight -20)) ++ ")"))
layoutPut layt dwnright 0 (myLayoutHeight -20)
dwnleft <- labelNew (Just ("+(" ++ (show(myLayoutWidth -70)) ++ "," ++
(show (myLayoutHeight -20)) ++ ")"))
layoutPut layt dwnleft (myLayoutWidth -70) (myLayoutHeight - 20)
labels <- sequence $ map (labelNew . Just) txtls
sequence_ $ map (\x -> widgetModifyFg x StateNormal (Color 0 0 45000)) labels
let wnums = zip labels [0..]
sequence_ $ map (myLayoutPut layt) wnums
widgetShowAll window
onDestroy window mainQuit
mainGUI
-- parameters
myLayoutWidth :: Int
myLayoutWidth = 800
myLayoutHeight :: Int
myLayoutHeight = 800
txtls :: [String]
txtls = map (\x -> x:[]) ['A'..'Z']
-- end parameters
step :: Double
step = (2 * pi)/(fromIntegral (length txtls))
ox :: Int
ox = myLayoutWidth `div` 2
oy :: Int
oy = myLayoutHeight `div` 2
radius :: Double
radius = 0.25 * (fromIntegral ox)
angle :: Int -> Double
angle num = 1.5 * pi + (fromIntegral num) * step
num2x :: Int -> Int
num2x n = ox + relx where
relx = round $ radius * (cos (angle n))
num2y :: Int -> Int
num2y n = oy + rely where
rely = round $ radius * (sin (angle n))
myLayoutPut :: Layout -> (Label, Int) -> IO ()
myLayoutPut lt (lb, n) = do
layoutPut lt lb (num2x n) (num2y n)
labelSetAngle lb (letterAngle n)
letterAngle :: Int -> Double
letterAngle n = (270 - degree) where
degree = (angle n) * (180.0 /pi)